Upper Endoscopy or EGD, Hemorrhoid Banding
Digestive health is vital for overall well-being, and timely medical intervention can prevent complications and improve quality of life. Two common gastrointestinal procedures that patients may require are upper endoscopy or EGD and hemorrhoid banding. Understanding these procedures, their purposes, and benefits helps patients make informed healthcare decisions.
Understanding Upper Endoscopy or EGD
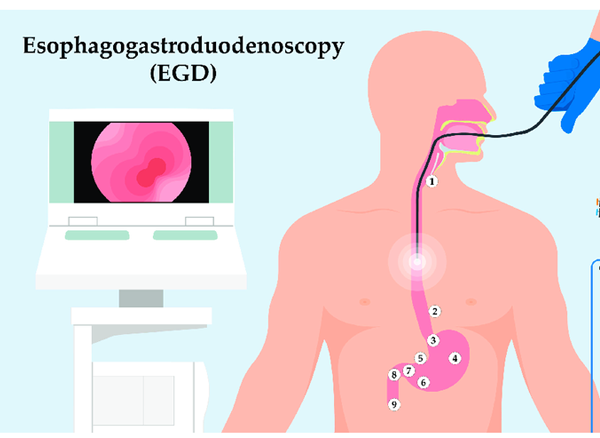
An upper endoscopy or EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the upper digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. During the procedure, a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to identify abnormalities, diagnose conditions, or perform certain treatments.
Key benefits of an upper endoscopy include:
- Accurate diagnosis: Detects ulcers, inflammation, bleeding, and tumors in the upper digestive tract.
- Biopsy capability: Allows tissue samples to be taken for further analysis.
- Therapeutic interventions: Certain conditions, such as bleeding ulcers or strictures, can be treated during the procedure.
- Minimally invasive: Reduces recovery time and minimizes discomfort compared to surgical alternatives.
Upper endoscopy is recommended for patients experiencing persistent heartburn, unexplained abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, or gastrointestinal bleeding. Early detection through an EGD can prevent serious complications and guide effective treatment plans.
Understanding Hemorrhoid Banding
Hemorrhoids, or swollen blood vessels in the rectal area, can cause discomfort, pain, and bleeding. Hemorrhoid banding is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure used to treat internal hemorrhoids by placing a small rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid shrinks and eventually falls off naturally.
Benefits of hemorrhoid banding include:
- Effective relief: Reduces pain, bleeding, and swelling associated with internal hemorrhoids.
- Quick procedure: Usually performed in a doctor’s office with minimal preparation.
- Minimal downtime: Patients can often resume normal activities shortly after treatment.
- Low complication rate: Safe and widely used for treating internal hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoid banding is ideal for patients who have not found relief through lifestyle changes or topical treatments. It provides a durable solution with minimal discomfort.
Combining Gastrointestinal Care
Both upper endoscopy or EGD and hemorrhoid banding illustrate the importance of proactive gastrointestinal care. While EGD focuses on diagnosing and treating upper digestive tract issues, hemorrhoid banding addresses lower digestive tract concerns. Together, these procedures highlight the range of minimally invasive options available for maintaining digestive health.
Tips for Patients
- Consult your physician: Discuss symptoms and determine which procedure is appropriate.
- Follow pre-procedure instructions: Proper preparation ensures accurate results and a smooth experience.
- Monitor recovery: Follow post-procedure care guidelines to prevent complications.
- Maintain digestive health: A balanced diet, hydration, and regular check-ups can reduce gastrointestinal problems.
Final Thoughts
Timely intervention is key to managing digestive health. Procedures like upper endoscopy or EGD and hemorrhoid banding offer safe, minimally invasive solutions for diagnosing, treating, and preventing gastrointestinal issues. By understanding these procedures, patients in need of care can make informed decisions, improve comfort, and protect their long-term digestive health.


